
Understanding Deviation in Forex Trading
Definition of Deviation
In forex, deviation represents the difference between an asset’s actual price movement and its anticipated trajectory based on historical data or technical indicators. Traders analyze these price discrepancies to assess volatility, understand market sentiment, and refine their strategies.
Factors Influencing Deviation
Several elements contribute to unexpected shifts in forex prices:
- Economic News & Data Releases: High-impact reports, such as Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP), inflation updates, and central bank decisions, frequently lead to significant price shifts.
- Market Sentiment: Changes in trader psychology, risk appetite, or geopolitical developments often result in sudden fluctuations.
- Trading Volume: Greater liquidity generally reduces extreme price swings, while lower volume can amplify erratic movements.
Importance of Deviation in Forex
Identifying Trends and Reversals
Understanding price discrepancies helps traders recognize potential trend shifts or confirm existing market directions. When price movements significantly diverge from expectations, it may indicate a possible reversal.
- Example: If an asset consistently trades above a moving average with increasing divergence, it could signal a strengthening trend. Conversely, sharp downward fluctuations below a key level might suggest an impending reversal.
Measuring Volatility
Tracking market fluctuations helps traders gauge volatility levels.
- High fluctuations: Indicate increased price swings, often caused by major economic events or news shocks.
- Low fluctuations: Suggest a more stable market with predictable short-term movements.
Traders factor in volatility to fine-tune their risk exposure, balancing opportunities in high-volatility environments with more stable trading conditions.
Standard Deviation in Forex Trading
What Is Standard Deviation?
Standard deviation is a statistical measure that quantifies the extent of price fluctuations from the mean over a specified period. In forex, it provides insights into market stability and potential breakout conditions.
The formula for standard deviation is:
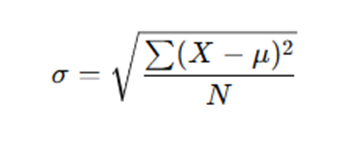
Where:
- X = Individual price points
- μ = Average price over a set timeframe
- N = Total number of data points
What Standard Deviation Reveals About Market Behavior
- High standard deviation: Indicates strong price swings, often signaling higher volatility and greater potential for breakout moves.
- Low standard deviation: Reflects a stable market with fewer price fluctuations, typically seen in ranging conditions.
An increasing standard deviation often precedes sharp market movements, while a declining measure suggests reduced momentum.

How Traders Use Deviation in Their Strategies
Positive and Negative Deviation
- Positive deviation: Occurs when the price moves beyond expectations in a favorable direction, presenting profit potential.
- Negative deviation: Arises when price performance falls short of forecasts, increasing downside risk.
By monitoring these shifts, traders adjust risk management strategies to minimize losses and capitalize on favorable price movements.
Applying Deviation to Entry and Exit Strategies
Price fluctuations influence how traders determine entry and exit points:
- Stop-Loss & Take-Profit Adjustments: Traders assess price variability to set protective orders, reducing exposure to abrupt market movements.
- Technical Analysis Tools: Bollinger Bands, which incorporate standard deviation, help visualize volatility and detect overbought or oversold conditions. A break beyond the upper or lower band often signals an impending reversal or continuation move.
By integrating volatility analysis into their approach, traders improve their ability to navigate market fluctuations with greater precision.

Practical Examples of Deviation in Forex Trading
Case Study: Using Deviation to Predict Market Swings
Consider the EUR/USD pair during a major economic release like the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) report. Ahead of the announcement, traders position themselves based on projected employment figures.
If the actual data significantly diverges from market expectations, price movements become more pronounced. For example:
- Stronger-than-expected NFP figures bolster USD demand, driving EUR/USD downward.
- Weaker NFP results weaken USD, leading to a sharp EUR/USD rally.
By analyzing past reactions to such reports, traders anticipate volatility and strategize accordingly.
How Professional Traders Adjust Their Positions Based on Deviation Data
Institutional traders monitor price variability through tools like Bollinger Bands and statistical channels. When price action repeatedly moves beyond predefined thresholds, they may:
- Modify stop-loss levels to avoid premature exits caused by market noise.
- Scale positions based on how fluctuations align with broader trend momentum.
- Combine volatility analysis with fundamental data to confirm trade setups.
For instance, during the Brexit referendum, GBP/USD experienced unprecedented price swings, prompting professional traders to hedge positions and adjust leverage to manage risk.

Common Mistakes Traders Make When Interpreting Deviation
Misjudging Volatility and Overleveraging
One of the most common mistakes is assuming that extreme price fluctuations always present lucrative trading opportunities. While high volatility can create potential profits, it also elevates risk.
Overleveraging in unpredictable markets can lead to severe losses if price movements become more erratic than anticipated. A trader using excessive margin in a volatile market might see their stop-loss triggered before the price resumes its intended direction. To mitigate this, traders should adjust position sizes in response to market conditions and avoid excessive risk exposure.
Relying Solely on Deviation Without Other Indicators
While tracking price variations is valuable, relying on it alone can lead to misleading conclusions. Significant fluctuations do not always indicate a trend reversal—they may simply reflect short-term market noise.
To enhance decision-making, traders should:
- Use complementary indicators like moving averages or the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
- Consider fundamental events that may explain price shifts (e.g., news catalysts).
- Validate trading signals with multiple sources before executing positions.
Conclusion
Monitoring price variations is essential in forex trading, helping traders evaluate volatility, manage risk, and refine their market approach. Whether applied to stop-loss adjustments, trend identification, or breakout predictions, understanding price fluctuations improves decision-making.
However, it should not be the sole determinant of trading actions. A well-rounded strategy that incorporates multiple analytical tools enhances accuracy and risk management. Traders who develop a balanced approach to market analysis will be better equipped to navigate forex price movements effectively.
Related Topics and Further Reading
How Market Sentiment Affects Forex Deviation
Trader sentiment—shaped by risk appetite, economic uncertainty, or geopolitical developments—can drive price swings beyond technical expectations. Understanding sentiment analysis can help anticipate abnormal movements.
The Role of Bollinger Bands in Measuring Deviation
Bollinger Bands, which rely on standard deviation, help traders assess price volatility. When prices break above or below the bands, it often signals potential overbought or oversold conditions, aiding in trade decisions.
Understanding ATR (Average True Range) and Its Connection to Deviation
ATR measures the average price range over a given period, providing another perspective on market volatility. Comparing ATR with standard deviation offers deeper insight into trading conditions.
FAQ
What does deviation mean on MT4?
On MT4, deviation refers to the allowable difference between a trader’s requested price and the actual execution price, helping to manage slippage. Traders can set thresholds to control execution slippage in volatile conditions.
What are deviations in trading?
In trading, deviations occur when price movements differ from historical patterns or expectations based on technical analysis. Traders use these variations to gauge volatility, assess market strength, and refine strategies.
What is currency deviation?
Currency deviation measures how much a forex pair’s price fluctuates from its expected or historical range. It is commonly analyzed using statistical tools like standard deviation to assess volatility and trading opportunities.